Understanding and maximizing the use of eutectic plates in the supply chain
9 January 2025 by Edina GÁLFI
28 August 2024 by Edina GÁLFI

Are you planning to start up a new food distribution business?
Home deliveries, food e-commerce, local producer? Whatever your plans are and the volumes you will be needing to distribute, you will be subject to the same obligations and you will need to think about the same issues.
In this feature, you will find all the answers to your questions so that you can get started with total peace of mind.
The cold chain consists of all the logistics and domestic operations intended to keep several specific products at their target temperature in order to guarantee their safety and their organoleptic qualities.
Maintaining the cold chain is a legal obligation because it is a public health matter.
In a judgment dating from 9 February 2016 the French Court of Cassation ruled that “a break in the cold chain renders the carrier liable even if the goods have not been damaged”. This means that any break in the cold chain can lead to having to pay the consignee damages which will vary in their amount according to the value of the goods lost.
ATP stands for “certificate for the transport of perishable foodstuffs” in French and is a mandatory certification for all vehicles carrying, within France, foodstuffs that need to be kept at the right temperature to retain their organoleptic properties.
It is based on an international agreement signed in 1976 by 48 countries around the world, and the ATP is obligatory:
The ATP is issued in France by Cémafroid, a private body mandated by the State.
ATP-certified vehicles provide you with guarantees on the thermal insulation performance of your equipment. Careful, though: insulating capability does not mean maintaining a low temperature. To do that, you have to have a cold source too.
In fact, insulating capacity or capability refers to technology that reduces the heat exchanged between the inside of a container and the external environment where it is situated or travelling.
The seriousness of the penalty is closely linked to the class to which your vehicle belongs. Nevertheless, in certain cases, travelling and transporting temperature-sensitive foodstuffs without an ATP can be considered as a criminal offence, subject to up to 2 years in prison and fines of up to €30,000.
Checks are unannounced and unpredictable and can be conducted by the police, customs, the fraud service, the gendarmerie, veterinary services, the DDPP (Departmental Directorate for the Protection of the Population) or any sworn agent.
The ATP certificate is valid for the first 6 years after your vehicle goes into service. After 6 years, you will need to renew it at a centre approved by Cémafroid. But this renewal is only valid for 3 years. You will therefore need to have your insulated vehicle tested again after 9 years on the road.
Different types of foodstuffs are divided into categories according to the temperature at which they need to be stored and transported :
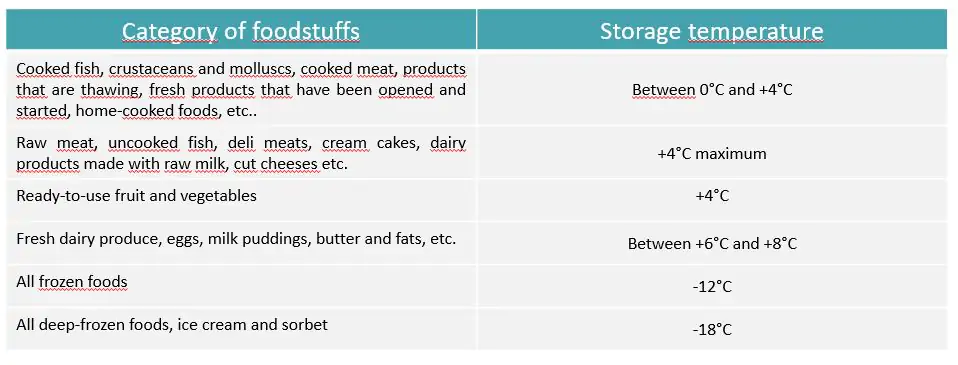
Be aware that this is only an extract. In fact, certain fragile products have to be kept at specific temperatures to slow the ripening process (e.g. bananas, red fruits, tomatoes).
Don’t hesitate it to contact us so that we can help you to define your cold chain. For every project, there is a logistics solution.
